Urinary Tract Infection
Overview
What is Urinary Tract Infection
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection in any part of your urinary system — your kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra. Most infections involve the lower urinary tract — the bladder and the urethra.
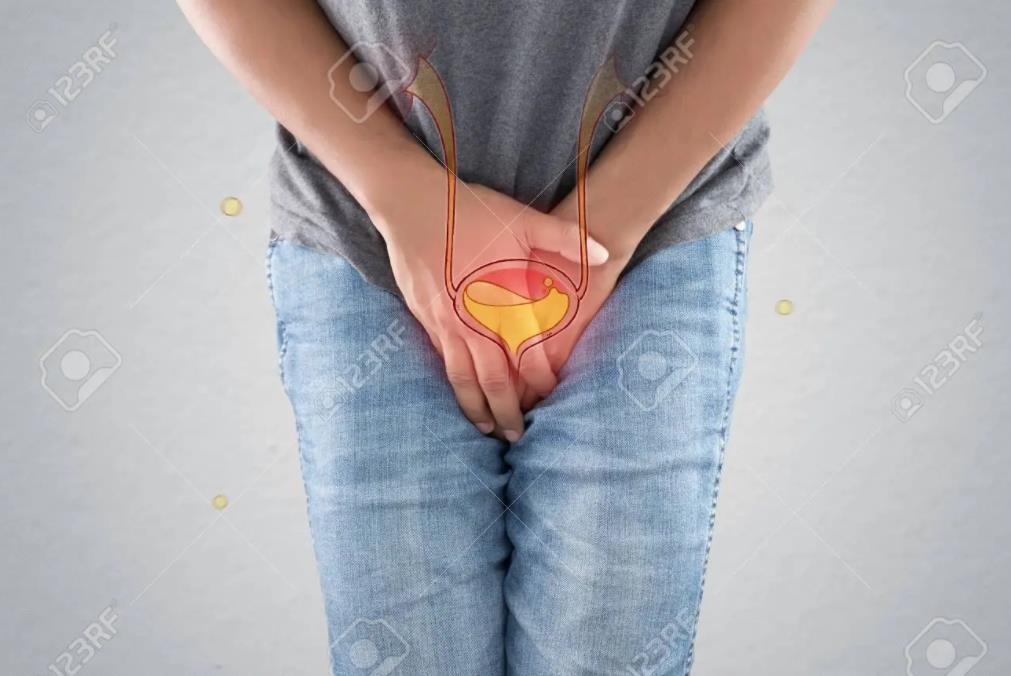
Symptoms
Urinary tract infections don’t always cause signs and symptoms, but when they do they may include:
- A strong, persistent urge to urinate
- A burning sensation when urinating
- Passing frequent, small amounts of urine
- Urine that appears cloudy
- Urine that appears red, bright pink or cola-colored — a sign of blood in the urine
- Strong-smelling urine
Causes
Urinary tract infections typically occur when bacteria enter the urinary tract through the urethra and begin to multiply in the bladder. Although the urinary system is designed to keep out such microscopic invaders, these defenses sometimes fail. When that happens, bacteria may take hold and grow into a full-blown infection in the urinary tract.
The most common UTIs occur mainly in women and affect the bladder and urethra.
- Infection of the bladder (cystitis): This type of UTI is usually caused by Escherichia coli (E. coli), a type of bacteria commonly found in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. However, sometimes other bacteria are responsible.
Diagnosis
Tests and procedures used to diagnose urinary tract infections include:
- Analyzing a urine sample: Your doctor may ask for a urine sample for lab analysis to look for white blood cells, red blood cells or bacteria. To avoid potential contamination of the sample, you may be instructed to first wipe your genital area with an antiseptic pad and to collect the urine midstream.
- Growing urinary tract bacteria in a lab: Lab analysis of the urine is sometimes followed by a urine culture. This test tells your doctor what bacteria are causing your infection and which medications will be most effective.
Treatment
Drugs commonly recommended for simple UTIs include:
- Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (Bactrim, Septra, others)
- Fosfomycin (Monurol)
- Nitrofurantoin (Macrodantin, Macrobid)
- Cephalexin (Keflex)
- Ceftriaxone
The group of antibiotic medicines known as fluoroquinolones — such as ciprofloxacin (Cipro), levofloxacin and others — isn’t commonly recommended for simple UTIs, as the risks of these medicines generally outweigh the benefits for treating uncomplicated UTIs.
